Cleaning water in factories isn’t just about following rules — it helps keep machines running, protects equipment, and saves the environment. Today, companies face increased pressure to reduce pollution and comply with stringent laws. Activated carbon is a reliable and versatile solution for purifying contaminated water using liquid filters.
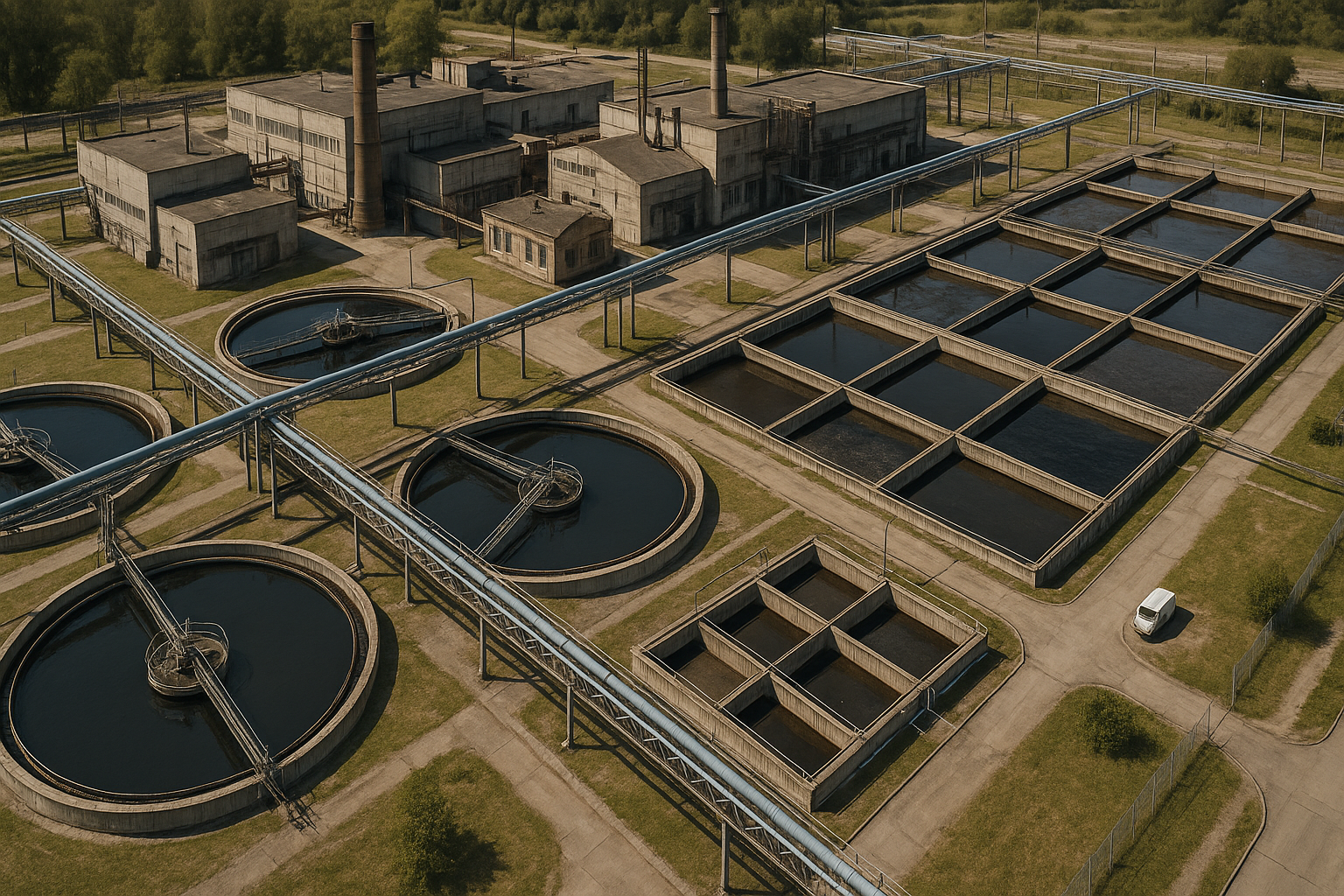

The picture is for reference only. Source: AI
Why Industrial Water Must Be Treated
Factories use water for:
- Cooling
- Cleaning
- Chemical reactions
- Making products
This water often becomes dirty and contains:
- Oils, solvents, and phenols
- Chlorinated chemicals and VOCs
- Dyes and color waste
- Soaps, pesticides, and medicine leftovers
- Heavy metals and small, harmful elements
If not cleaned, these can cause:
- Damage to machines
- Lower work efficiency
- Legal trouble
- Harm to nature and people
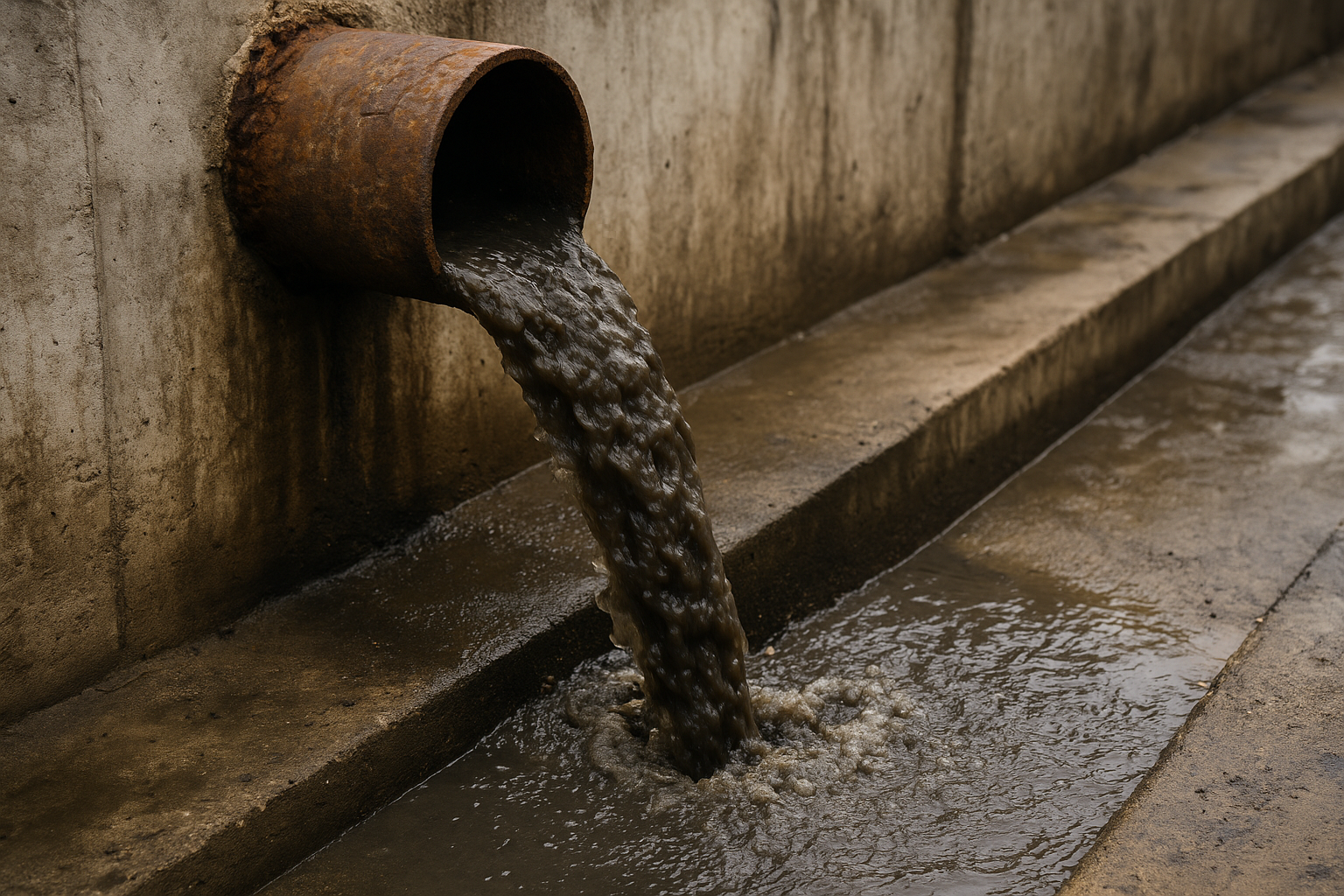

The picture is for reference only. Source: AI
How Activated Carbon Works
Activated carbon traps dirty substances on its surface. Its tiny holes pull in and hold different kinds of molecules. That’s why it works well with many types of factory wastewater.
| What It Has |
What It Does |
| Large surface area |
Grabs many types of pollutants |
| Tiny holes of different sizes |
Catches both small and big particles |
| Different grain sizes available |
Fits different types of filter systems |
| Can be reused |
Cuts cost and waste with reactivation |
The picture is for reference only. Source: AI
Where It’s Used
1. Chemical and Oil Industry
- Use: Cleans water, removes solvents, and chlorine
- Why: Keeps products clean and protects materials
2. Textile and Dye Factories
- Use: Takes out color and dye leftovers
- Why: Meets rules and allows water reuse
3. Food and Drink Factories
- Use: Removes bad tastes, smells, and dirt
- Why: Improves product quality
4. Medicine and Cosmetic Plants
- Use: Removes drug and chemical remains
- Why: Meets health and safety rules
5. Mining and Metal Work
- Use: Treats water with cyanide, phenols, and metals
- Why: Reduces harm and lets water be used again
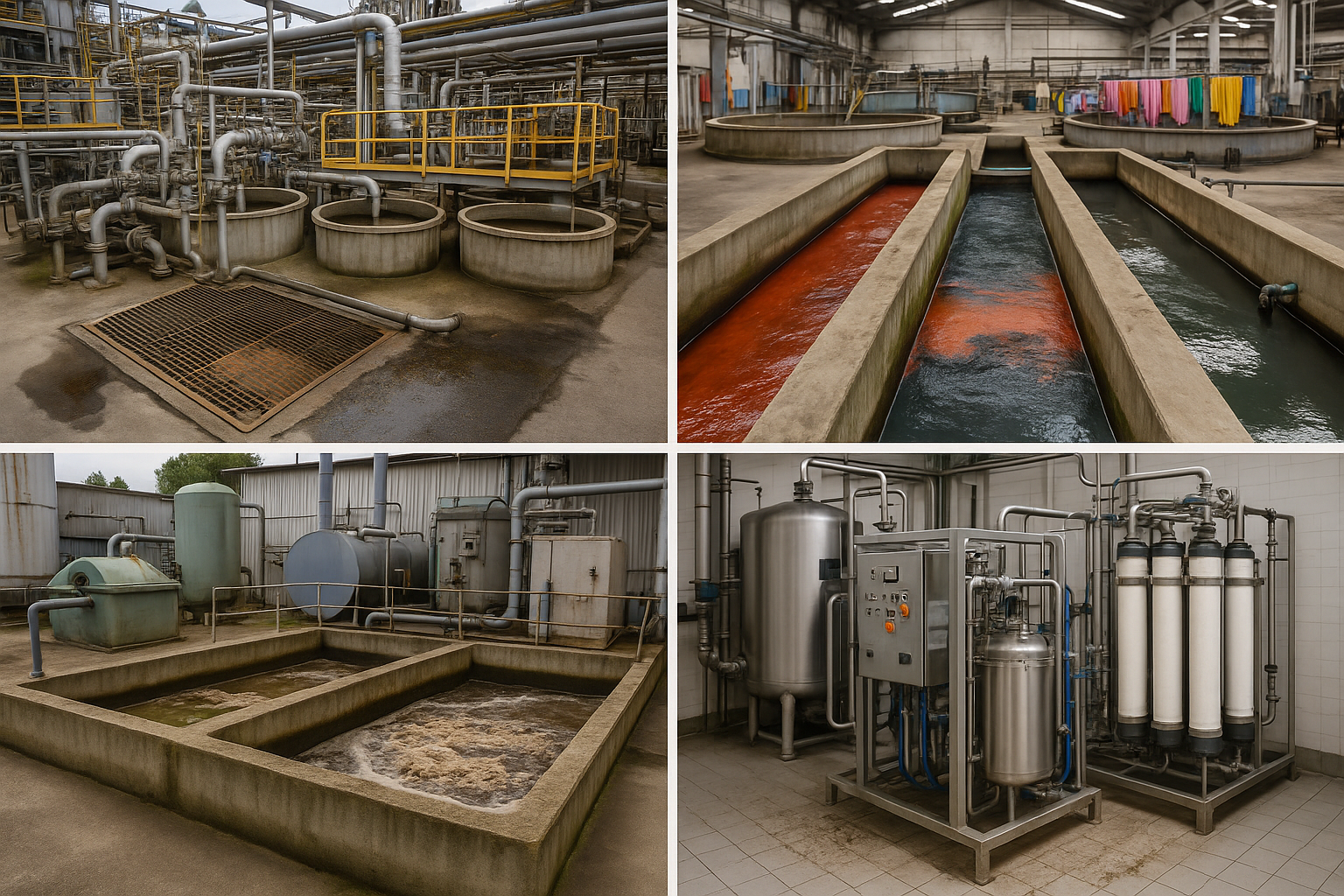

The picture is for reference only. Source: AI
Reuse and Sustainability
Used carbon can be heated and reused, keeping up to 95% of its strength. This helps:
- Cut down on waste
- Save money
- Lower the impact on the planet
Some factories even reuse their carbon on-site in closed systems.

The picture is for reference only. Source: AI
What Affects System Design
| Thing to Consider |
Why It Matters |
| Type of pollution |
Affects how long carbon must stay in contact |
| Flow speed of water |
Decides how big the system should be |
| Water pH and temperature |
Changes how well carbon works |
| Type of carbon (GAC or PAC) |
GAC for ongoing use, PAC for one-time use |

The picture is for reference only. Source: AI
Problems and How to Avoid Them
What Can Go Wrong:
- Water flows unevenly through the carbon
- Germs grow in carbon beds
- Carbon gets full without warning
What to Do:
- Test the water regularly
- Filter out dirt before it reaches the carbon
- Set a schedule to clean or change the carbon
- Watch for pressure changes in the system

The picture is for reference only. Source: AI
Meeting the Rules
Activated carbon helps companies follow rules from:
- EPA (USA)
- OSHA (USA)
- REACH (EU)
This helps companies:
- Avoid fines
- Stay eco-friendly
- Build trust with the public
The Future of Carbon Use
New tech is making activated carbon smarter and greener:
- Special carbon made for certain pollutants
- Systems that mix carbon with other filters
- Intelligent tools that warn when carbon is used up
Summary: Why Activated Carbon Matters
| Strength |
What It Means |
| Removes many pollutants |
Keeps water clean and safe |
| Flexible and useful |
Works in many industries |
| Can be reused |
Cuts cost and waste |
| Trusted by experts |
Used worldwide for industrial water cleaning |

The picture is for reference only. Source: AI








